So what exactly is biochar?

So what exactly is biochar?
Biochar is a sustainable form of charcoal made from biomass – organic matter, such as agricultural crop residues, wood waste and animal manure. Historically, it has been produced for thousands of years dating back to a civilization in the Amazon Basin.
Nowadays, there is a rising global interest in biochar as it is increasingly being recognised as a multi-purpose, sustainable material offering numerous benefits to both urban and rural environments around the world.
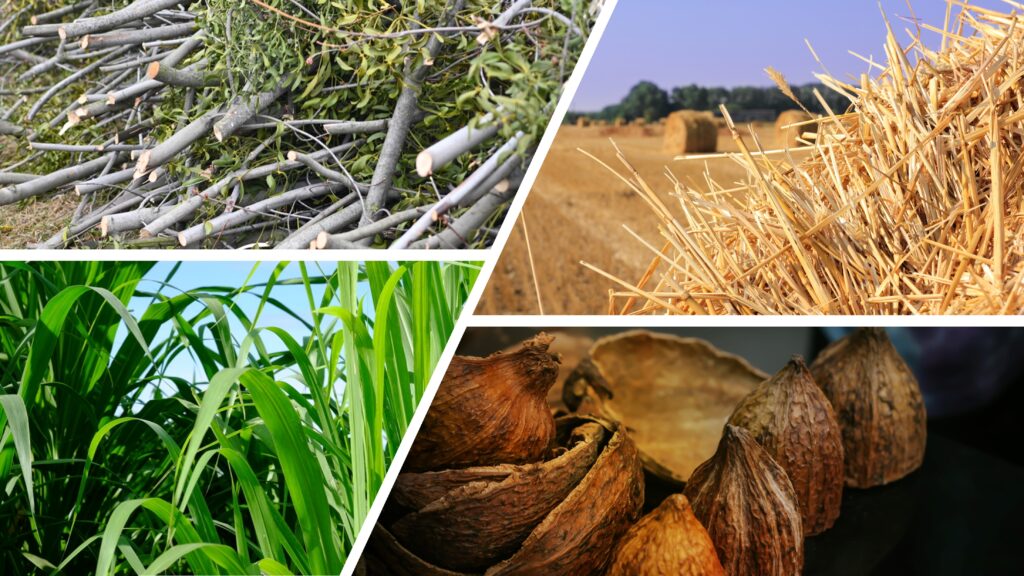

Pictured here is a selection of biomass feedstocks which can be used to produce biochar.
Top left: waste wood cuttings.
Top right: cocoa husks.
Bottom left: agricultural straw.
Bottom right: Miscanthus x giganteus – elephant grass.
How is it produced?
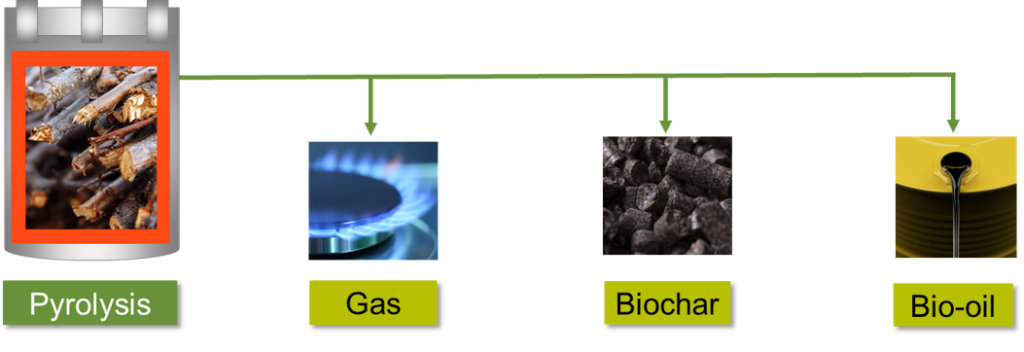
Biochar is produced by a thermal conversion process, known as pyrolysis, which heats the biomass material at temperatures between 300 and 800oC in an oxygen-free atmosphere. This process produces three valuable byproducts: gas, liquid and biochar – the lightweight black residue, rich in carbon.
The physical and chemical properties of biochar are determined by:
- Biomass feedstock used
- Production temperature
- Residence time (time spent inside process vessel)
- Scale of method adopted ranging from large-scale stationary pyrolysis units to smaller-scale retort chambers, kilns and stoves
nefits and use of biochar
 Benefits and uses of biochar
Benefits and uses of biochar
Carbon-rich biochar offers a wide variety of benefits and uses in both rural and urban environments. With its porous structure, it adsorbs and holds gases, odours, organic nutrients, and environmental contaminants. It offers many applications including:
 Soil improvement
Soil improvement
Sometimes referred to as ‘Horticultural Charcoal’, biochar when added to soil can increase plant and tree growth and health; result in higher crop yields; as well as help carbon/water/nutrient retention.
 Carbon sequestration
Carbon sequestration
Biochar not only increases soil carbon sequestration, when it is used in material applications such as bioplastics, it can offset several tonnes of CO2 per tonne of product manufactured.
 Animal feed additive
Animal feed additive
Biochar can not only be used in improving the health and digestion processes of animals such as cattle, it can potentially reduce ammonia emissions from animals, reducing the impact livestock has on contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
 Activated carbon
Activated carbon
Activated carbon is a form of carbon processed to have a higher surface area available for adsorption of chemicals, pollutants or contaminants. It increases the commercial value of the biochar and offers many industrial applications including:
-
- Water treatment
- Water filtration
- Air purification
 Construction materials
Construction materials
Emerging applications for biochar include:
-
- Asphalt for roads
- Soil stabilisation in roads
- Urban applications, such as rainwater management for pathways
- Building materials including composites, plaster, insulation materials and green roofs
- Concrete
- Plastic composites
Other byproducts
The thermal treatment process of pyrolysis also produces gases and liquids (besides the biochar) which offer a number of commercially valuable opportunities such as:
 Low carbon fuel for boilers and engines
Low carbon fuel for boilers and engines
 Bioliquids such as wood vinegar for low carbon weedkiller, fungicide and plant growth enhancer
Bioliquids such as wood vinegar for low carbon weedkiller, fungicide and plant growth enhancer




